
By understanding these characteristics, you’ll be able to shop with confidence
DIAMOND EDUCATION
This Diamond Education defines the four most essential characteristics of diamond along with tips for its care.
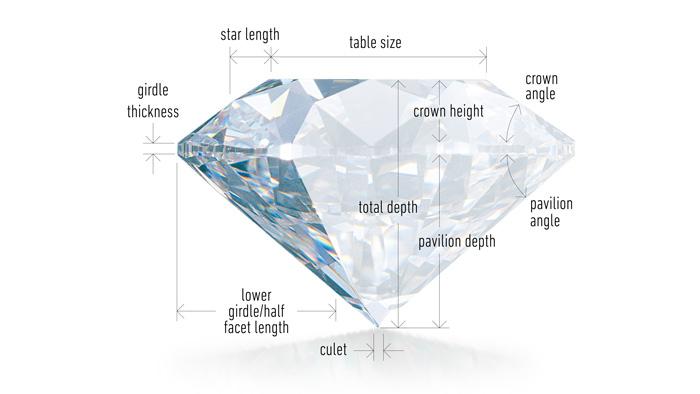
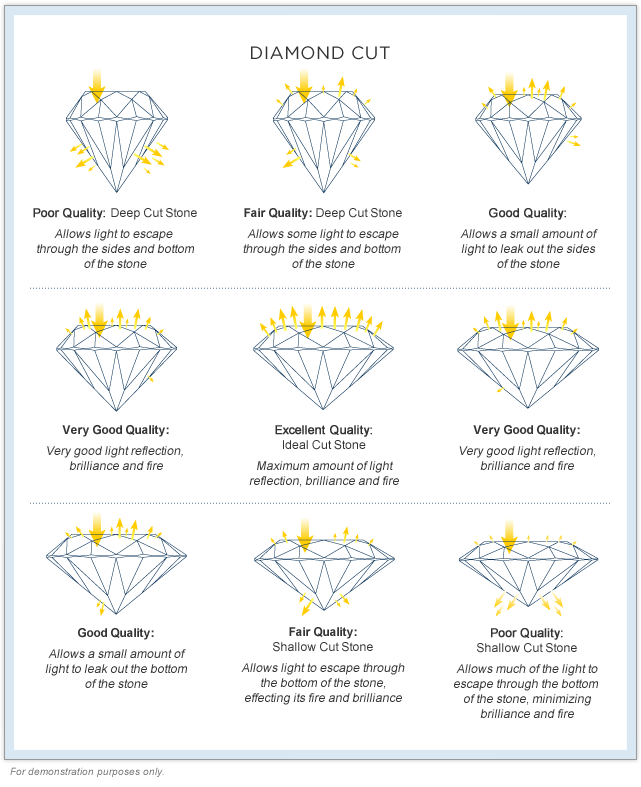
When a stone is cut, every effort is made to ensure its proportions are either ideal, excellent or at least very good
DIAMOND CUT
If the diamond is cut too shallow in height, light can be lost as is passes straight through.
If the Diamond is cut too deep, light can be lost through its sides. An ideal cut diamond allows light to enter into the diamond and reflect of its internal surfaces and bounce straight back out offering a scintillating light effect to the observer
As the diamond is moved into and out of light sources the varying directions of the light will seem to dance off it surface in a colorful array Many diamonds are cut to ensure that their proportions are perfect for this natural light play. The more brilliant and bright a diamond is the more ideal it is
If care and attention are taken for its symmetry as well as the quality of its polished surfaces these add even great brightness and and fire to its observer
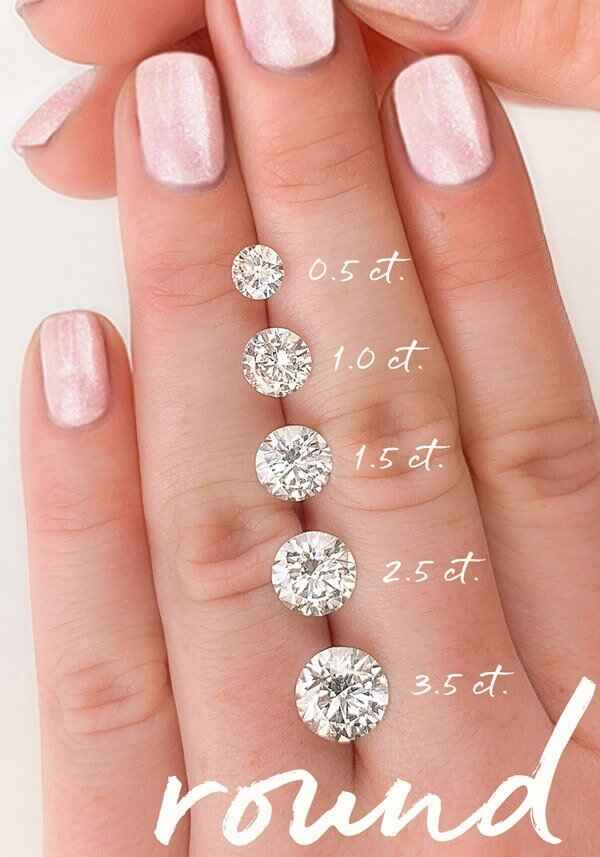

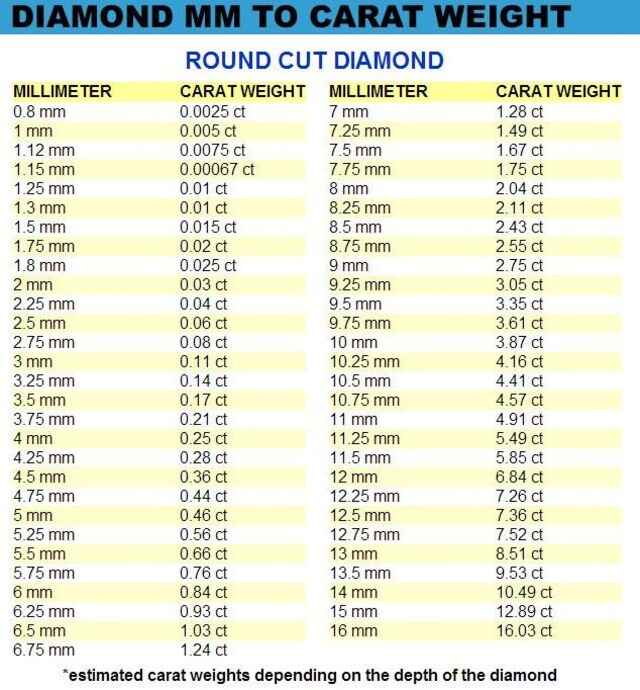
The metric weight of a diamond is collectively known as the Carat (ct)
DIAMOND CARAT
A metric carat is defined as 200 milligrams. The size of the diamond will increase with the carat weight. The larger the carat weight the more rare the diamond. Therefore diamond prices increase exponentially with the carat weight
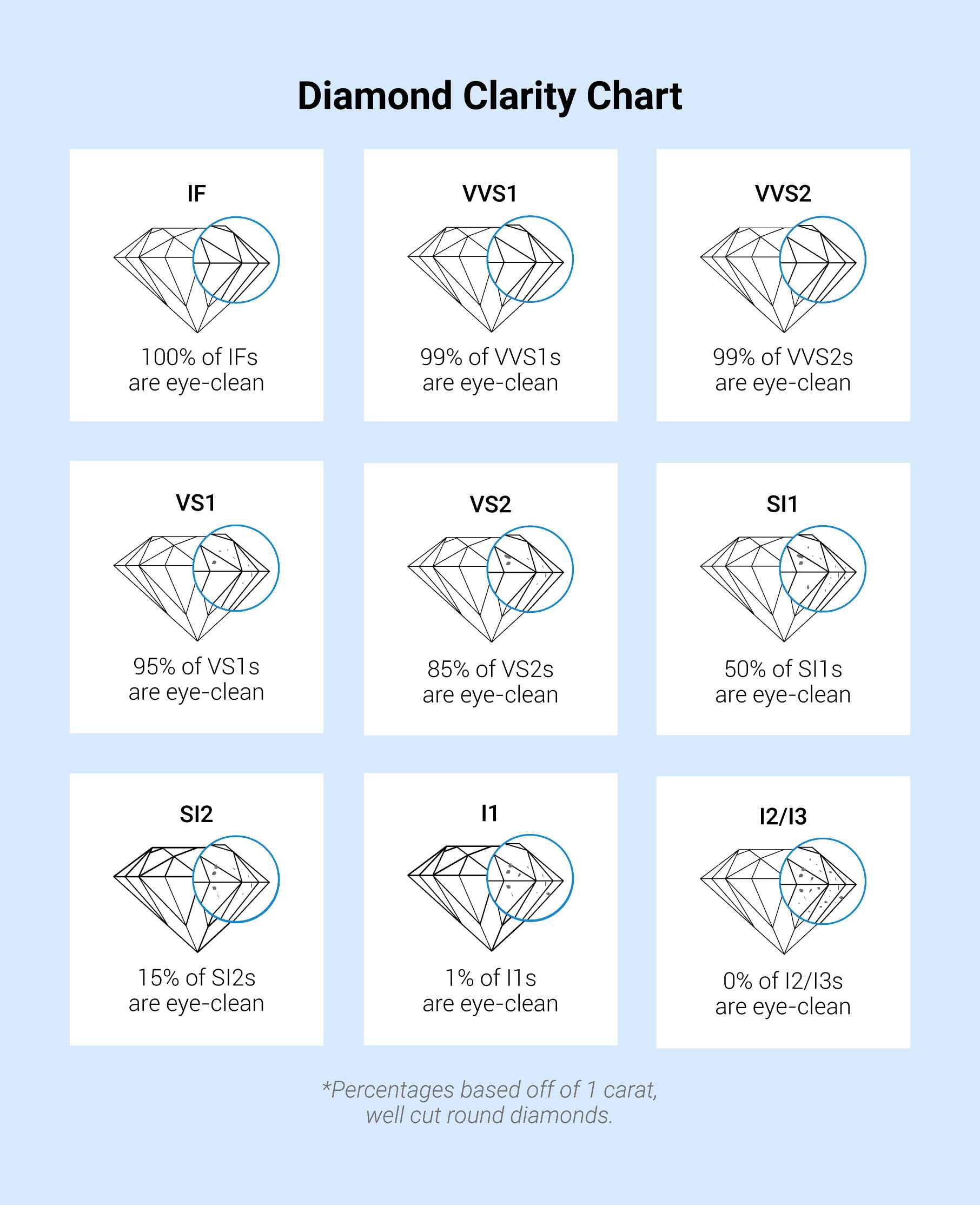
DIAMOND CLARITY
The IF Grade (Internally Flawless) A diamond which has no internal characteristics but which, due to minor finish faults, is not flawless and therefore cannot be designated FL or flawless, may be called IF or internally flawless provided the finish faults are so minute that they can be removed by a gentle polishing with only an insignificant loss of weight
The VVS Grades (Very, Very Small Inclusions) The term VVS is used for diamonds with internal characteristics very, very difficult for a qualified observer to find under observation conditions as described. Further, there may only be insignificant finish faults
The VS Grades (Very Small Inclusions) The term VS is used for diamonds in which it is difficult for a qualified observer, under observation conditions as described, to find either a few somewhat larger internal characteristics or several very small ones
The SI Grades (Small Inclusions) The term SI is used for diamonds in which a qualified observer may, without difficulty, under observation conditions as described, find internal characteristics. Further, there may only occur single finish faults of an insignificant kind

Only a Gemologist can detect the differences in colour between the top graded diamonds. Diamonds graded from K-Z will have a visible warm pale yellow hue. To avoid a diamond with a yellow hue choose a diamond graded as H or higher
Fancy coloured diamonds including yellows, pink, and blue diamonds are graded using a different colour scale
DIAMOND COLOR
Diamonds occur naturally in a wide variety of colours. White diamonds are graded alphabetically from D to Z according to a white colour scale. The letter D is the most colourless diamond and appears white. An increasing amount of pale yellow tint is present as the letters progress from D towards Z
Diamonds graded G-H are known as ‘near colourless’ diamonds
All of the diamonds we sell are graded as minimum H colour. H colour diamonds are also better value because they are colourless and much less expensive that diamonds graded G or above.It is recommended that diamonds graded as F or above are set in white gold or platinum settings to avoid tinting from the yellow gold setting
